Last Updated on July 21, 2023 by Laura Thompson
Rabbits are adorable pets that bring joy to many households. However, like any other animal, they are susceptible to certain health issues, including lice infestations. Lice are external parasites that feed on the blood of rabbits and cause itching, irritation, and other health problems. In this article, we will explore the question “can rabbits get lice?” and provide you with the information you need to keep your furry friend healthy and happy.
Lice infestations in rabbits are not very common, but they can occur. These parasites are host-specific, which means that rabbits can only get rabbit lice, and humans cannot get lice from their pet rabbits. However, it is still important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of lice infestations in rabbits, as they can cause discomfort and even lead to more serious health problems if left untreated. In the next section, we will discuss the signs and symptoms of lice infestations in rabbits, so you can identify them early and take action to treat them.
Can Rabbits Get Lice?
As a pet owner, it’s important to be aware of the potential health issues that can affect your furry friend. One such issue is lice infestation, which is relatively common in rabbits. In this section, we’ll explore what lice are, the types of lice that can infect rabbits, the symptoms of lice infestation, how to diagnose and treat it.
What are Lice?
Lice are small, wingless parasites that feed on the blood of their host. They are host-specific, meaning that rabbit lice will only infest rabbits and cannot be transmitted to humans or other animals. Lice infestations are most common in rabbits kept in poor hygienic conditions, such as dirty cages or bedding.
Types of Lice in Rabbits
There are two main types of lice that can infest rabbits: biting lice and sucking lice. Biting lice feed on the fur and skin of their host, while sucking lice feed on their blood. Both types of lice can cause discomfort and irritation to rabbits, leading to scratching, itching, and hair loss.
Symptoms of Lice Infestation in Rabbits
The symptoms of lice infestation in rabbits can vary depending on the severity of the infestation. Common signs include itching and scratching, hair loss, and visible lice or eggs in the fur. In severe cases, rabbits may also experience anemia, weight loss, and weakness.
Diagnosis of Lice Infestation in Rabbits
If you suspect that your rabbit has lice, it’s important to take them to a veterinarian for diagnosis. A vet will examine your rabbit’s fur and skin for visible signs of lice or eggs. They may also perform a skin scraping or fur pluck to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Lice Infestation in Rabbits
The treatment of lice infestation in rabbits typically involves a combination of medication and environmental management. Your vet may prescribe medication such as ivermectin or selamectin to kill the lice and their eggs. It’s also important to clean the cage and bedding thoroughly to remove any remaining lice or eggs. Regular grooming and cleaning can help prevent future infestations.
Lice infestation is a common problem in rabbits that can cause discomfort and irritation. However, with proper treatment and management, it can be easily treated and prevented. If you suspect that your rabbit has lice, it’s important to take them to a veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment.
Preventing Lice Infestation in Rabbits
Lice can be a real problem for rabbits, causing discomfort and skin irritation. However, there are several steps you can take to help prevent lice infestation in your furry friend.
Cleaning the Cage
Keeping your rabbit’s cage clean is essential for preventing lice infestation. Regularly cleaning the cage and removing any soiled bedding or droppings will help to eliminate any potential breeding grounds for lice. You should also ensure that your rabbit’s living area is well-ventilated and not too humid, as lice tend to thrive in warm, damp environments.
Grooming and Hygiene
Regular grooming is another important step in preventing lice infestation in rabbits. Brushing your rabbit’s fur can help to remove any loose hairs and debris that might attract lice. Additionally, keeping your rabbit’s fur clean and dry can help to prevent lice from taking hold. However, be careful not to bathe your rabbit too often, as this can strip their skin of its natural oils and make them more susceptible to lice infestation.
Maintaining good hygiene practices is also important for preventing lice infestation. Washing your hands thoroughly before and after handling your rabbit can help to prevent the spread of lice. Additionally, keeping your rabbit’s food and water bowls clean and free of debris can help to prevent lice from taking hold.
Environmental Factors
Finally, environmental factors can also play a role in preventing lice infestation in rabbits. Keeping your rabbit’s living area free of clutter and debris can help to eliminate any potential hiding places for lice. Additionally, using natural deterrents such as cedar chips or eucalyptus leaves in your rabbit’s living area can help to repel lice and other pests.
By following these simple steps, you can help to prevent lice infestation in your rabbit and keep them happy and healthy.
Other Parasites That Affect Rabbits
Rabbits are prone to various parasites that can affect their health and well-being. In addition to lice, there are other parasites that can infest rabbits. Here are some of the most common ones:
Fleas

Fleas are blood-sucking parasites that can cause itching, skin irritation, and anemia in rabbits. They are usually introduced into the rabbit’s environment by other pets, such as dogs and cats, or by wild animals. Fleas can be treated with topical or oral medications that kill the parasites.
Mites
Mites are tiny parasites that can cause skin irritation, hair loss, and scabs in rabbits. There are several types of mites that can infest rabbits, including ear mites, fur mites, and mange mites. Mites can be treated with topical or oral medications that kill the parasites.
Ticks
Ticks are blood-sucking parasites that can transmit diseases to rabbits. They are usually found in wooded areas or tall grasses and can attach themselves to the rabbit’s skin. Ticks can be removed with tweezers or a tick remover tool. It is important to remove the entire tick, including the head, to prevent infection.
Ear Mites
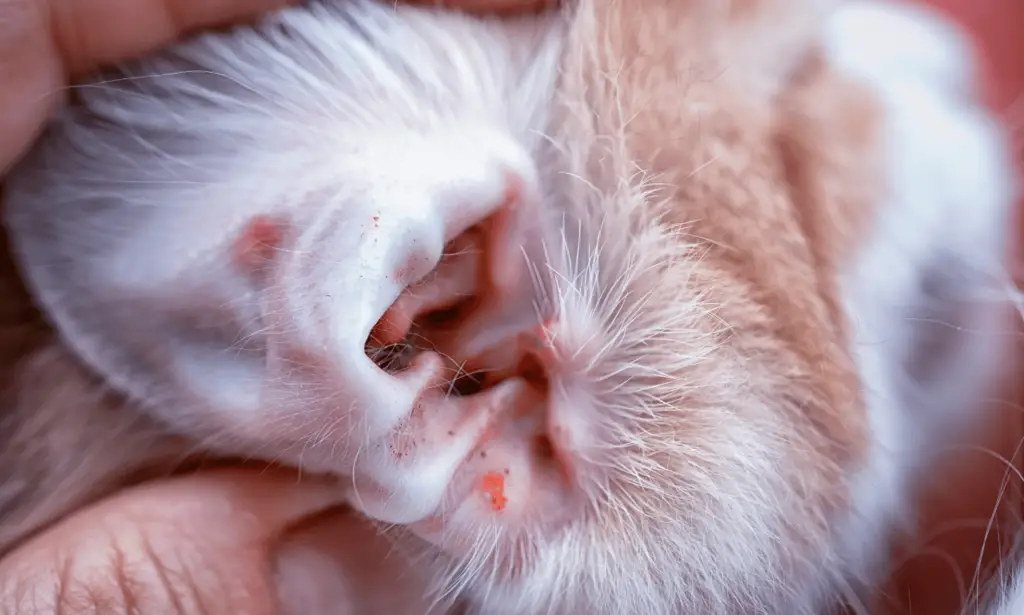
Ear mites are tiny parasites that live in the ears of rabbits. They can cause itching, head shaking, and ear discharge. Ear mites can be treated with topical or oral medications that kill the parasites.
Cheyletiella
Cheyletiella, also known as walking dandruff, is a type of mite that can infest rabbits. It causes itching and flaky skin. Cheyletiella can be treated with topical or oral medications that kill the parasites.
Tapeworms
Tapeworms are intestinal parasites that can infect rabbits. They are usually introduced into the rabbit’s environment through contaminated food or water. Tapeworms can cause weight loss, diarrhea, and poor coat condition. They can be treated with oral medications that kill the parasites.
Rabbits are susceptible to various parasites that can cause health problems. It is important to keep their environment clean and free of parasites, and to seek veterinary care if your rabbit shows signs of infestation.
Other Diseases and Conditions That Affect Rabbits
Rabbits are susceptible to various diseases and conditions that can cause discomfort and even death. As a responsible pet owner, it is essential to be aware of these conditions and take appropriate measures to prevent and treat them. Here are some of the most common diseases and conditions that affect rabbits.
Myxomatosis
Myxomatosis is a viral disease that is transmitted by fleas, mosquitoes, and other biting insects. It causes swelling and discharge from the eyes, nose, and anus, and can lead to respiratory distress, fever, and death. There is no cure for myxomatosis, and infected rabbits should be isolated to prevent the spread of the disease.
Ringworm
Ringworm is a fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails of rabbits. It causes circular, scaly patches of skin and can be transmitted to humans. Ringworm is treatable with antifungal medication, but it can take several weeks to clear up completely.
Coccidia
Coccidia are microscopic parasites that can infect the intestines of rabbits. They cause diarrhea, weight loss, and dehydration, and can be fatal in young or immunocompromised rabbits. Coccidia can be prevented by keeping the rabbit’s environment clean and dry and providing fresh water and food.
Trauma
Rabbits can be easily injured by falls, bites, or accidents. Trauma can cause broken bones, internal bleeding, and other serious injuries. If a rabbit has been injured, it should be taken to a veterinarian immediately for treatment.
Liver Disease
Liver disease can be caused by a variety of factors, including poor diet, infections, and toxins. It can cause jaundice, weight loss, and lethargy. Treatment for liver disease depends on the underlying cause and may include medication, dietary changes, and supportive care.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can affect the skin, nails, and respiratory system of rabbits. They can be caused by a variety of fungi and can cause itching, hair loss, and respiratory distress. Fungal infections can be treated with antifungal medication and by keeping the rabbit’s environment clean and dry.
As a rabbit owner, it is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of these diseases and conditions and to take appropriate measures to prevent and treat them. Regular veterinary check-ups, a healthy diet, and a clean living environment can go a long way in keeping your rabbit healthy and happy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Laura is an experienced wildlife rehabilitator and conservationist residing in Madison, Wisconsin. Her love for rabbits was sparked during her early career when she nursed an injured wild rabbit back to health. Today, she runs “Hoppy Haven”, a rehabilitation center dedicated to the care and release of injured wild rabbits.
